Table of Contents
Introduction:
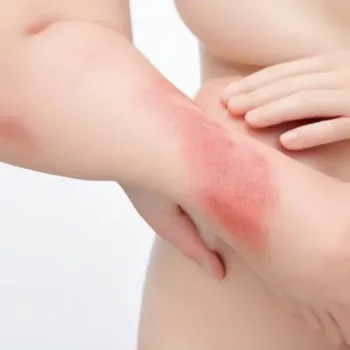
Eczema, also known as dermatitis, is a common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Characterized by red, itchy, and inflamed skin, eczema can vary in severity and often leads to discomfort and a decreased quality of life for those affected. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of eczema, exploring its causes, symptoms, and effective management strategies.
What is Eczema?
It is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that results in the skin becoming red, itchy, and irritated. It is not contagious and can affect people of all ages, from infants to adults. There are several types , with atopic dermatitis being the most common form. Other types include contact dermatitis, dyshidrotic eczema, and nummular eczema, each with its unique characteristics and triggers.
you can also read about Acne Causes, Types, Treatment Strategies, and Skincare Tips click here
Causes and Risk Factors:
While the exact cause of eczema is not fully understood, a combination of genetic and environmental factors is believed to play a significant role. Individuals with a family history of eczema, asthma, or hay fever may be more predisposed to developing the condition. Environmental factors such as exposure to certain irritants, allergens, or harsh weather conditions can also trigger or exacerbate symptoms.
- Genetic Factors: It often has a genetic component. Individuals with a family history of eczema, asthma, or allergic rhinitis are more likely to develop eczema themselves. Specific genetic variations can affect the skin’s barrier function and immune response, increasing susceptibility to eczema.
- Immune System Dysfunction: It is associated with an overactive immune system response. In individuals with eczema, the immune system may react excessively to certain triggers, leading to inflammation and skin symptoms.
- Skin Barrier Dysfunction: The skin acts as a barrier that protects the body from irritants and allergens. In people with eczema, the skin barrier is compromised, allowing irritants to penetrate more easily and triggering an immune response. This compromised barrier also leads to increased water loss, contributing to dry and itchy skin.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain environmental factors can exacerbate its symptoms. Common triggers include:
1.Allergens: Pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and mold.
2. Irritants: Harsh soaps, detergents, certain fabrics, and skincare products.
3.Temperature and Humidity: Extreme temperatures and low humidity can worsen eczema symptoms.
4.Microbes: Bacteria, viruses, and fungi can contribute to skin infections, which may exacerbate it. - Dry Skin: Individuals often have drier skin, which can lead to increased sensitivity and a higher likelihood of developing eczema symptoms.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, particularly during puberty and pregnancy, can influence eczema symptoms. Hormones can affect the skin’s barrier function and immune response.
- Stress: Stress is known to trigger or exacerbate eczema symptoms. The connection between stress and it is complex and likely involves hormonal and immune system responses.
- Certain Foods:While rare, certain foods may act as triggers in some individuals. Common culprits include dairy, eggs, nuts, and seeds. However, food triggers can vary from person to person.
- Scratching and Rubbing: Itching is a hallmark symptom and the act of scratching or rubbing the affected areas can worsen inflammation and contribute to the cycle of eczema flares.
- Microbial Factors: Changes in the skin microbiome, including an imbalance of beneficial and harmful bacteria on the skin, may play a role in eczema development.
- Exposure to Chemicals:Contact with certain chemicals, such as perfumes, dyes, and preservatives in skincare products, may trigger or exacerbate eczema in some individuals.
Symptoms:
The symptoms can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common symptoms include:
- Itching: Persistent and intense itching is a hallmark symptom of eczema. Scratching the affected areas can worsen the condition and lead to skin damage.
- Redness and Inflammation: The skin may become red, swollen, and inflamed, particularly during flare-ups.
- Dry and Cracked Skin: It can cause the skin to become dry, rough, and prone to cracking, especially in areas with frequent scratching.
- Blisters and Oozing: In some cases, it can lead to the formation of small blisters that may ooze or weep fluid.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosing eczema typically involves a thorough examination of the patient’s medical history and a physical examination of the affected skin. In some cases, patch testing may be conducted to identify specific allergens triggering the condition.
Management and Treatment:
While there is no cure for it , various management strategies can help control symptoms and improve the quality of life for individuals with the condition. These include:
- Topical Steroids and Moisturizers: Topical corticosteroids are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation, itching, and redness. Regular use of emollients and moisturizers helps to keep the skin hydrated.
- Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding triggers, such as certain allergens or irritants, is crucial in managing it. This may involve changes in lifestyle, diet, or the use of hypoallergenic products.
- Antihistamines: Oral antihistamines can be prescribed to help alleviate itching and improve sleep quality, especially if itching is disrupting sleep.
- Phototherapy: In some cases, exposure to controlled amounts of ultraviolet (UV) light under medical supervision may be recommended to manage its symptoms.
- Immunosuppressants: For severe cases, systemic medications like immunosuppressants may be prescribed to modulate the immune response and reduce inflammation.
Lifestyle and Prevention:
Adopting a healthy lifestyle and taking preventive measures can contribute to managing it . This includes:
- Gentle Skin Care: Using mild, fragrance-free cleansers and avoiding hot water can help maintain skin health.
- Cotton Clothing: Wearing loose-fitting, breathable cotton clothing can reduce irritation and allow the skin to breathe.
- Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate its symptoms. Practicing stress-reduction techniques such as meditation or yoga may be beneficial.
Conclusion:
Eczema is a common and chronic skin condition that requires ongoing management. While there is no cure, effective treatment and lifestyle adjustments can significantly improve symptoms and enhance the overall well-being of individuals living with it . Seeking the guidance of a healthcare professional is essential for proper diagnosis and personalized management strategies tailored to each individual’s needs.
for more information click here

